A list of websites appears when you Google something, such as “best coffee shop near campus.” Most likely, you click on one of the first few results. Except in extreme cases, very few people scroll to page three. SEO can help with that.
The process of making a website better so that it appears higher on search engine results pages (SERPs) is known as search engine optimization, or SEO. Simply put, more people are likely to visit your website if it ranks higher, and you don’t have to pay for advertisements to get them there.
But it’s not magic. Algorithms are used by search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo to determine which pages show up first. Understanding what those algorithms are searching for and aligning your website as closely as possible with their expectations is the goal of SEO.
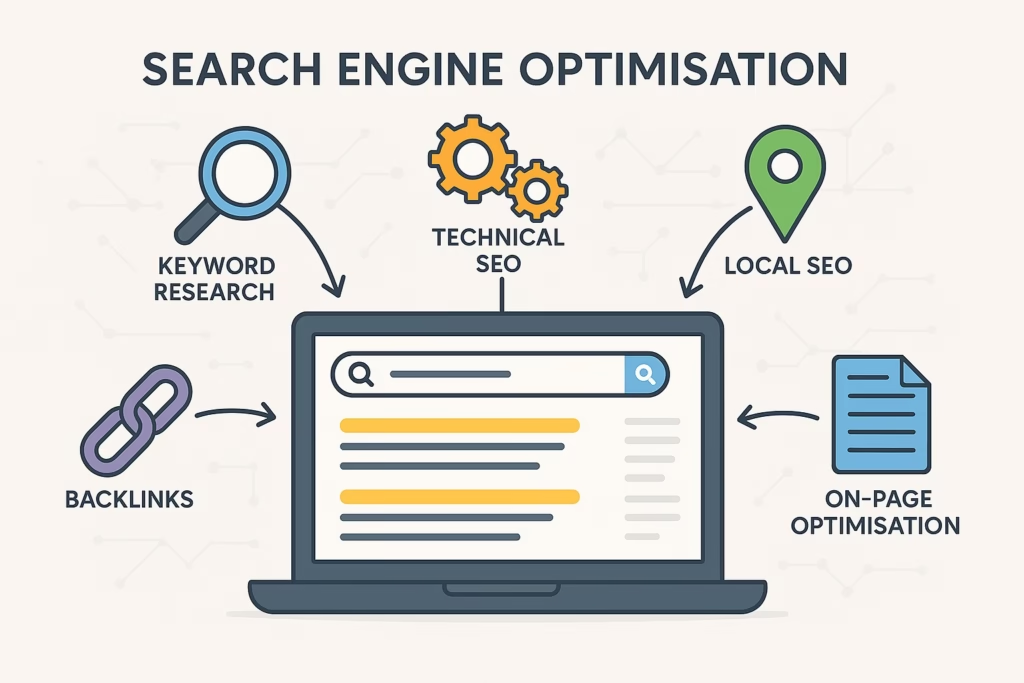
I think of SEO as a cycle rather than a one-time task. It usually involves these steps:
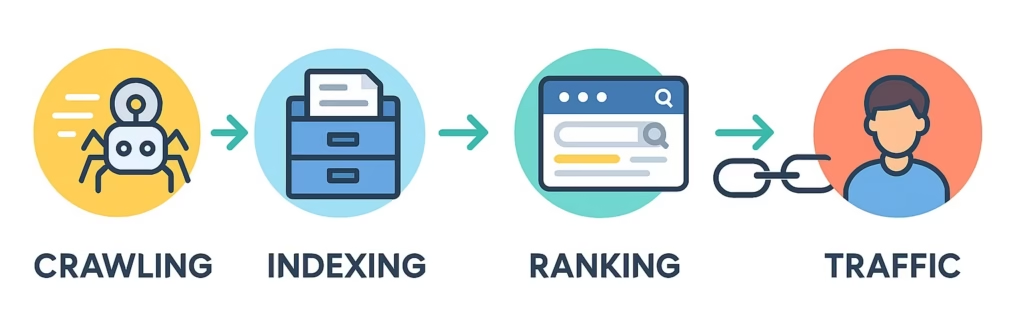
Search engines use programs called “crawlers” or “spiders” to scan the internet. These bots find pages, read them, and store the information in a massive index. After finding and reading pages, these bots compile the data into a sizable index.
Search engines cannot see your page if it is not in the index. People simply won’t find it, just like if you had a store without any signage.
For instance, Google’s bots will eventually “crawl” a website you publish if you own a new bakery and add it to their database. However, the bots may never find your site if there are no links pointing to it.
Google attempts to determine what users are looking for when they type something into the search engine. Are they seeking to visit a particular website (“Sourdough.com”), make a purchase (“buy sourdough starter”), or obtain information (“how to bake sourdough”)?
It’s critical to align your content with the user’s intent. Google is aware that visitors will leave your bakery website if it attempts to rank for “how to bake sourdough” but only provides your prices.
This is where you make changes to your website’s pages’ content and organization to make them easier for both humans and bots to understand. This comprises:
Keywords: The words and phrases people type into search engines.
Titles and Headings: It is evident what is important when content is arranged using H1, H2, and H3 tags.
Meta Descriptions: The brief excerpt that appears beneath the title of your page in Google.
Images are described by image alt text for search bots and accessibility.
For instance, on a page about the “Best Coffee Beans in London,” you may inadvertently use words like “Arabica,” “roast,” and “brewing” without feeling crowded.
This is about establishing the reputation of your website outside of your own pages. Backlinks, or when other websites link to yours, are the most important factor here.
An endorsement from a reputable website is akin to a vote of confidence. Google views you as more reliable the more high-quality votes you have.
It’s similar to real life in that people are more likely to trust you if a well-known food blogger endorses your bakery.
If your website is difficult to use on mobile devices or loads slowly, even the best content won’t rank well. Technical SEO includes topics such as:
If you were at a restaurant with delicious food but a door that wouldn’t open, you would probably leave. Online, the same thing.
SEO is not “set and forget.” Your rivals are constantly attempting to outrank you, and search engines are always changing their algorithms. Google Analytics and Google Search Console are two tools that assist in tracking what is and is not working.
For instance, Google may have changed its guidelines or someone else may have published something better if your “Best Coffee Beans” page is suddenly losing visitors. You would have to adjust and get better.
Each of the several primary “flavours” of SEO has a distinct focus. The majority of companies use a combination.
It all comes down to making your website’s content as good as possible.
It includes:
On-page SEO is in play if the article “How to Make the Perfect Cappuccino” on your bakery blog is clear, informative, and well-organized.
This is mostly about using backlinks to increase credibility.
Among the tactics are:
Most inexperienced website owners overlook this behind-the-scenes stuff, but it has the power to make or break rankings.
It includes topics such as:
If your business depends on nearby customers, local SEO is a game-changer.
It entails making your website and online presence as search engine friendly as possible so that locals find you first.
This comprises:
This kind of online store optimization concentrates on making sure that product pages, descriptions, and images are optimized to appear in search results.
In order to show prices and ratings in search results directly, you also need to consider category pages, product filters, and even schema markup.
The primary factor that makes SEO so beneficial is that it attracts “organic” traffic, or visitors who find your website naturally rather than through sponsored advertisements.
Because they are actively searching for what you have to offer, this traffic is frequently more valuable than random visitors.
If your website appears highly when someone searches for “order custom birthday cakes,” they are most likely ready to make a purchase rather than just perusing.
SEO is a combination of art and science. Making your website the most relevant, practical, and reliable choice for whatever your target audience is looking for is more important than trying to trick Google.
The rewards can be enormous, but it takes time—months at times. You can continue to receive traffic without continuously purchasing advertisements once your website is ranked highly.
The most crucial mentality, in my opinion, is to prioritize people over algorithms. You’re halfway there if your website is actually clear, helpful, and simple to use.
Crawling: Bots from search engines locate and examine your website.
Indexing: Data is kept in a database so that it can be found later.
Search Intent: Aligning your content with what people are genuinely searching for is known as search intent.
On-Page SEO: Optimizing text, headings, images, and structure is known as on-page SEO.
Off-Page SEO: Using mentions and backlinks to establish credibility.
Technical SEO: Enhancing the security, usability, and speed of websites.
Continuous Process: Needs ongoing observation and revision.
On-Page SEO: Optimizing specific web pages (keywords, headings, and content quality) is known as on-page SEO.
Off-Page SEO: Obtaining links from PR, brand mentions, and other reliable websites is known as off-page SEO.
Technical SEO: Enhancements made behind the scenes to increase the effectiveness of crawling and indexing.
Local SEO: Local search engine optimization, or SEO, is crucial for physical businesses.
E-Commerce SEO: Optimizing product and category pages for online retailers is known as e-commerce SEO.
Hi, I’m Manimaran – I write short notes and study tools that help you revise faster, remember better, and succeed with confidence.
Stuuddt: Access short notes, unit summaries, study tips, and exam boosters all in one place
Free Download Our Stuuddy Materials 100% Off!